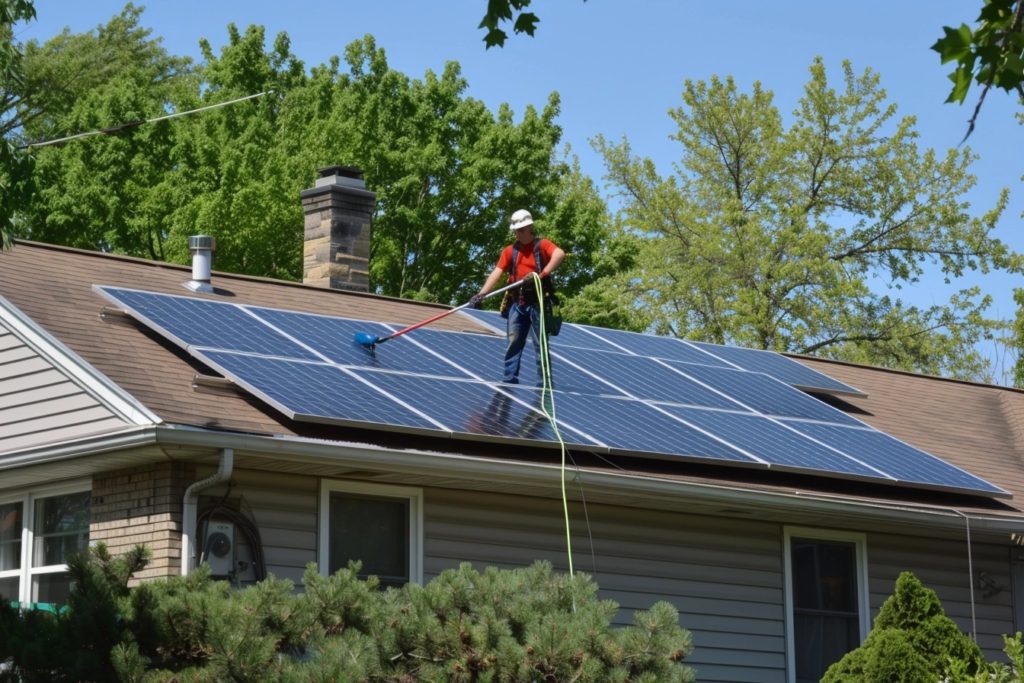
Residential solar power has been gaining traction across the United States as more homeowners seek to reduce energy costs and embrace renewable energy. However, the adoption of solar energy varies significantly from state to state. Here’s a countdown from 50 to 1, with 1 being the state with the most residential solar installations in 2024.
50. North Dakota
49. West Virginia
48. South Dakota
47. Montana
46. Nebraska
45. Wyoming
44. Alaska
43. Idaho
42. Mississippi
41. Alabama
40. Kentucky
39. Arkansas
38. Louisiana
37. Missouri
36. Indiana
35. Kansas
34. Ohio
33. Tennessee
32. Iowa
31. Michigan
30. Oklahoma
29. Minnesota
28. Wisconsin
27. Pennsylvania
26. Illinois
25. Virginia
24. South Carolina
23. Nevada
22. Oregon
21. Washington
20. New York
19. Maryland
18. Connecticut
17. Georgia
16. Massachusetts
15. Colorado
14. New Jersey
13. Texas
12. Arizona
11. North Carolina
10. Utah
9. Rhode Island
8. Vermont
7. Florida
6. Hawaii
5. Delaware
4. Nevada
3. New Mexico
2. California
1. Texas
Why Do Some States Lead in Solar Adoption?
Several factors contribute to why certain states rank higher in residential solar adoption:
Sunlight Availability: States like California, Texas, and Florida naturally have more sunlight, making solar energy more viable and attractive. The high solar irradiance ensures that solar panels operate at their full potential.
Incentive Programs: States that rank high typically offer robust incentive programs that make solar installation more affordable. For instance, New Jersey’s Successor Solar Incentive (SuSI) program provides substantial financial incentives, including payouts for generated solar energy. Similarly, Massachusetts has a strong Solar Renewable Energy Credit (SREC) market that incentivizes solar production.
Net Metering: States with favorable net metering policies, like California and New York, allow homeowners to sell excess electricity back to the grid at favorable rates, making solar installations financially beneficial.
High Electricity Rates: In states like Hawaii and Connecticut, the high cost of electricity makes solar power an economically attractive alternative, leading to quicker payback periods for solar installations.
State Policies and Renewable Energy Goals: Many leading states have aggressive renewable energy mandates or goals. California, for instance, has set ambitious targets for renewable energy, which has spurred widespread adoption of solar power.
Economic Incentives: Many states provide grants, rebates, and tax incentives that reduce the upfront costs of solar installations. This financial support is crucial for many homeowners who might otherwise find the initial investment too steep.
Conclusion
The variation in solar adoption across the United States is largely driven by a combination of natural, economic, and policy factors. States with abundant sunshine, strong policy support, and high electricity costs tend to see the highest adoption rates. As more states introduce favorable policies and as the cost of solar continues to fall, we can expect these rankings to evolve, with more states moving up the list.
10 reasons we’ve heard customers say they love solar.
10. Community Impact
Going solar can inspire others in the community to consider renewable energy options. It fosters a culture of sustainability and environmental responsibility, creating a positive ripple effect.
9. Energy Security
Solar energy can contribute to a more secure energy future. By diversifying our energy sources and reducing reliance on imported fuels, solar power enhances national energy security.
8. Job Creation
The solar industry is a significant source of job creation. By going solar, individuals support an industry that provides employment opportunities in manufacturing, installation, and maintenance.
7. Low Maintenance
Solar panels require minimal maintenance. With no moving parts, they are durable and can last a long time with little upkeep, providing a hassle-free energy solution.
6. Technological Advancements
Advancements in solar technology have made panels more efficient and affordable than ever before. Innovations continue to improve the performance and aesthetics of solar systems, making them an attractive option for more homeowners.
5. Possible Government Incentives
Many governments offer incentives, such as tax credits and rebates, to encourage the adoption of solar energy. These financial incentives can significantly offset the initial cost of installing solar panels.
4. Potential for Increased Property Value
Homes equipped with solar panels can often see an increase in property value. Potential buyers are attracted to the prospect of lower energy bills and the eco-friendly benefits of solar energy.
3. Energy Independence
With solar panels, homeowners can produce their own electricity, reducing their dependence on the grid. This independence can be particularly valuable during power outages or in remote areas where grid access is limited if they have batteries as well.
2. Environmental Impact
Solar energy is a clean, renewable resource that reduces our reliance on fossil fuels. By going solar, individuals can significantly lower their carbon footprint and contribute to a healthier planet.
1. Savings on Energy Bills
One of the most compelling reasons people switch to solar energy is the potential for savings on their electricity bills. By generating their own power, homeowners can often reduce their monthly energy costs.
Switching to solar energy offers a multitude of benefits, from financial savings to environmental stewardship. It’s no wonder more and more people are making the switch and loving the results!
What do you think? Are you considering going solar too? 🌞
Investing in residential solar panels is an excellent way to reduce your carbon footprint and save on electricity costs. However, the amount of money you can save depends significantly on the number of sun hours your location receives. This blog post will explore how sun hours affect your solar savings and what factors you should consider when evaluating the potential benefits of residential solar.
Understanding Sun Hours
Sun hours, also known as peak sun hours, refer to the amount of sunlight a location receives in a day, measured in hours of maximum solar radiation. One peak sun hour is equivalent to 1,000 watts of solar energy per square meter of solar panel per hour. This metric is crucial because it directly impacts the amount of electricity your solar panels can generate.
Geographic Location
Your geographic location is the primary determinant of the number of sun hours you receive. Areas closer to the equator typically enjoy more consistent and intense sunlight throughout the year, leading to higher solar energy production. For example, southern states in the U.S., such as Arizona and California, receive more sun hours compared to northern states like Washington or New York.
Seasonal Variations
Sun hours can also vary with the seasons. In many regions, the summer months bring longer days and more intense sunlight, leading to higher solar energy production. Conversely, winter months have shorter days and less sunlight, which can reduce the efficiency of your solar panels. Understanding these seasonal variations can help you estimate the annual solar output and potential savings.
Solar Panel Orientation and Tilt
The orientation and tilt of your solar panels can significantly impact the number of effective sun hours they receive. Ideally, solar panels should be installed facing true south in the northern hemisphere (or true north in the southern hemisphere) to maximize sun exposure. The tilt angle should be adjusted according to your latitude to capture the maximum amount of sunlight throughout the year.
Local Climate and Weather Patterns
Local climate and weather patterns also play a crucial role in determining sun hours. Areas with frequent cloudy or rainy days will have reduced sun hours compared to regions with clear, sunny skies. While occasional clouds won’t drastically affect your solar savings, consistently overcast conditions can lead to lower energy production and savings.
Shading and Obstructions
Shading from trees, buildings, or other obstructions can significantly reduce the number of sun hours your solar panels receive. Even partial shading can cause a disproportionate drop in solar panel efficiency. Conducting a thorough shading analysis before installation can help you identify and mitigate potential shading issues to maximize your sun hours and savings.
Calculating Solar Savings
To estimate your solar savings, you need to consider the average number of peak sun hours your location receives and the efficiency of your solar panels. Most solar panels have an efficiency rating that indicates the percentage of sunlight they can convert into electricity. By multiplying the average daily sun hours by the total capacity of your solar system and its efficiency, you can estimate the amount of electricity your system will generate.
For example, if you live in an area that receives an average of 5 peak sun hours per day, and you have a 5 kW solar system with an efficiency of 20%, your daily electricity generation would be:
5 hours/day × 5kW × 0.20 = 5kWh/day
5 hours/day×5 kW×0.20=5 kWh/day
By comparing this figure to your daily electricity consumption, you can estimate your potential savings.
Maximizing Your Solar Savings
To maximize your solar savings, consider the following tips:
- Optimal Installation: Ensure your solar panels are installed at the best orientation and tilt for your location.
- Regular Maintenance: Keep your solar panels clean and free from debris to maintain their efficiency.
- Monitor Shading: Regularly check for new shading from growing trees or new constructions and address any issues promptly.
- Energy Efficiency: Complement your solar system with energy-efficient appliances and habits to reduce overall consumption.
Conclusion
Sun hours play a pivotal role in determining the effectiveness and savings of residential solar systems. By understanding and optimizing factors such as geographic location, seasonal variations, panel orientation, and local climate, you can maximize your solar energy production and achieve significant cost savings. Investing in residential solar is not just about harnessing the power of the sun; it’s about making smart choices to ensure you get the most out of your solar investment.
Embrace the power of solar energy and start your journey toward sustainable living and financial savings today!
Solar panels convert sunlight into electricity through a fascinating process called the photovoltaic effect. Here’s how it works:
The Photovoltaic Effect
At the heart of solar energy conversion is the photovoltaic (PV) cell, the basic building block of a solar panel. These cells are typically made from silicon, a semiconductor material. When sunlight strikes a PV cell, it initiates a series of events:
- Photon absorption: Sunlight is composed of tiny packets of energy called photons. When these photons hit the PV cell, they are absorbed by the semiconductor material.
- Electron excitation: The absorbed photons energize electrons within the silicon atoms, causing them to break free from their atomic bonds.
- Electron flow: The PV cell is designed with two layers of silicon – one positively charged (p-type) and one negatively charged (n-type). This creates an electric field that directs the flow of freed electrons, generating an electric current.
- Electricity generation: The movement of these electrons creates a direct current (DC) of electricity.
From Cell to Panel to Array
Individual PV cells are combined to form solar panels, which can then be connected into larger arrays:
- A single PV cell typically produces only 1 or 2 watts of power.
- Multiple cells are electrically connected and packaged into a solar panel (or module).
- Panels can be further combined into arrays to increase the total power output.
Converting DC to AC
The electricity generated by solar panels is direct current (DC), but most household appliances and the power grid use alternating current (AC). To address this:
- Inverters are used to convert the DC electricity from the panels into AC electricity.
- This AC electricity can then be used to power homes, businesses, or fed back into the electrical grid.
Efficiency and Advancements
The efficiency of solar panels has improved significantly over time:
- In the mid-1980s, commercial PV panels averaged less than 10% efficiency.
- By 2015, this had increased to around 15%.
- Today, state-of-the-art modules are approaching 25% efficiency.
- Experimental PV cells for specialized applications have achieved nearly 50% efficiency.
Applications and Benefits
Solar energy has a wide range of applications, from powering small calculators to providing electricity for entire communities. The benefits of solar power include:
- Clean, renewable energy production with no harmful emissions during operation.
- Reduced dependence on fossil fuels and lower carbon footprint.
- Potential for significant cost savings on electricity bills over time.
- Contribution to a more resilient and diversified energy grid.
As technology continues to advance and costs decrease, solar energy is playing an increasingly important role in the global transition to clean, sustainable energy sources. The ability to harness the sun’s vast energy potential through the simple yet ingenious process of photovoltaics represents a bright future for renewable energy.
As energy costs continue to rise, finding effective ways to reduce your energy bill becomes increasingly important. At LGCY Power, we understand the value of conserving energy and saving money. Here’s our countdown our 10 favorite ways to save on your energy bill, culminating in the ultimate energy-saving solution.
10. Switch to LED Lighting
Swapping out traditional incandescent bulbs for LED lighting is a simple yet impactful change. LED bulbs use up to 80% less energy and last significantly longer, reducing both your energy consumption and replacement costs.
Does Unplugging Electronics Save on Electricity?
9. Use Smart Power Strips
Many electronics continue to draw power even when turned off. Smart power strips cut off the electricity supply to devices that are in standby mode, effectively eliminating “phantom” energy use and saving you money over time.
What runs your electricity bill up the most?
8. Install a Programmable Thermostat
Heating and cooling account for nearly half of the average household’s energy bill. A programmable thermostat allows you to set specific temperatures for different times of the day, ensuring that you’re not wasting energy when you’re not home or while you sleep.
7. Optimize Your Water Heater
Lowering the temperature on your water heater to 120 degrees Fahrenheit can save energy and reduce costs. Additionally, insulating your water heater and the first six feet of hot and cold water pipes can improve efficiency.
6. Seal and Insulate Your Home
Proper insulation and sealing of gaps and cracks in your home prevent heat from escaping in the winter and cool air from leaking out in the summer. This reduces the workload on your heating and cooling systems, resulting in lower energy consumption.
5. Use Energy-Efficient Appliances
When it’s time to replace old appliances, choose those with the Energy Star label. These appliances meet strict efficiency guidelines and can use up to 50% less energy than their non-efficient counterparts.
4. Maximize Natural Light
Take advantage of natural light by keeping blinds and curtains open during the day. This reduces the need for artificial lighting and can help to heat your home in the winter, lowering both lighting and heating costs.
3. Perform Regular HVAC Maintenance
Regular maintenance of your heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) system ensures it runs efficiently. Clean filters, unobstructed vents, and professional tune-ups prevent your system from working harder than necessary, saving energy and extending its lifespan.
2. Use Ceiling Fans Wisely
Ceiling fans can help circulate air and reduce the need for heating and cooling. In the summer, set fans to spin counterclockwise to create a cooling breeze. In the winter, set them to spin clockwise at a low speed to push warm air down from the ceiling.
1. Invest in Solar Energy
And our favorite way to save money on your energy bill is through solar energy. Solar panels harness the power of the sun to generate electricity, significantly reducing or possibly eliminating your reliance on traditional power sources. With solar energy, you can lock in lower energy costs, potentially increase your property value, and contribute to a more sustainable future.
What’s the Most Efficient Way to Save on Electricity?
By implementing these energy-saving strategies, you can reduce your energy consumption, lower your bills, and make a positive impact on the environment. From simple changes like switching to LED bulbs to transformative solutions like installing solar panels, each step you take contributes to greater savings and a more energy-efficient home. At [Solar Company Name], we’re here to help you achieve your energy-saving goals. Contact us today to learn more about how solar energy can benefit you.
Is Illinois Phasing Out Net Metering?
In Illinois, net metering is undergoing significant changes starting January 1, 2025, particularly for Ameren customers. Here are the key points:
Reduced Net Metering Benefits: For new solar customers who install panels after January 1, 2025, the net metering benefit will be reduced. While current net metering provides credits on the entire electric bill (supply, delivery, taxes, and fees), after the changes, new customers will only receive credits on the supply portion of their bill (Illinois Power Agency) (Citizens Utility Board).
Grandfathering Existing Customers: Customers who have already installed solar panels and have been approved for net metering before the end of 2024 will continue to receive the full net metering benefits for the life of their system, which is typically defined as 30 years.
What is the Net Metering Limit in Illinois?
Distributed Generation Rebate: New solar customers after January 1, 2025, will be eligible for a Distributed Generation (DG) Rebate. This rebate requires the use of a smart inverter and provides an upfront financial benefit to offset the reduced net metering credits. The rebate amount will be at least $300 per kilowatt of generating capacity.
What is the Deadline for Full Benefits? To take advantage of the current full net metering benefits, customers must have their solar systems installed, interconnected, and receive permission to operate from the utility by December 31, 2024. Specific deadlines for documentation submissions to ensure timely approval have been set by utilities like Ameren and ComEd.
These changes are part of Illinois’ broader transition towards a value-based compensation framework for solar energy, reflecting the state’s increasing adoption of solar power and the legislative adjustments planned under the Future Energy Jobs Act of 2016.
*Sources Illinois Power Agency & Citizens Utility Board
As the world shifts towards more sustainable energy sources, the United States has seen a significant increase in residential solar adoption. Homeowners across the country are harnessing the power of the sun to reduce their electricity bills and their carbon footprint. Here, we explore the top ten U.S. states leading the way in residential solar adoption, counting down from ten to one.
10. New York
New York has made significant strides in solar energy adoption, driven by ambitious renewable energy goals and incentives. The state’s NY-Sun Initiative provides financial incentives for residential solar installations. New York also offers net metering and tax credits, encouraging homeowners to switch to solar power.
9. Colorado
Colorado’s sunny climate and supportive policies have made it a hub for residential solar energy. The state offers incentives such as the Residential Renewable Energy Rebate Program and property tax exemptions. Colorado’s commitment to renewable energy has led to a growing number of homeowners installing solar systems.
8. Massachusetts
Massachusetts has been a leader in renewable energy adoption for years. The state’s Solar Massachusetts Renewable Target (SMART) program provides incentives for residential solar installations, making it financially viable for homeowners. Massachusetts also offers net metering and tax credits, further boosting solar adoption.
7. New Jersey
New Jersey is a surprising contender in the residential solar market, thanks to its progressive energy policies and incentives. The state offers one of the most generous Solar Renewable Energy Certificate (SREC) programs in the country, allowing homeowners to earn credits for the energy their systems produce. New Jersey also has strong net metering policies and various state incentives.
6. Nevada
Nevada’s abundant sunshine and supportive policies make it a hotspot for residential solar adoption. The state offers incentives such as net metering, rebates, and property tax exemptions for solar installations. Nevada’s commitment to renewable energy has led to a significant increase in residential solar systems.
5. North Carolina
North Carolina has emerged as a leader in solar energy in the southeastern United States. The state’s Renewable Energy and Energy Efficiency Portfolio Standard (REPS) requires utilities to source a portion of their energy from renewable sources, boosting residential solar installations. North Carolina also offers tax credits and other incentives to support solar energy.
4. Arizona
Arizona’s sunny climate makes it a perfect location for solar energy. The state has implemented policies to encourage solar adoption, including tax credits, rebates, and a robust net metering system. Arizona’s Solar Equipment Certification ensures that installed systems meet high standards of efficiency and reliability.
3. Florida
The Sunshine State lives up to its nickname with a strong commitment to solar energy. Florida’s residential solar market has grown rapidly due to favorable weather conditions and supportive policies. The state offers incentives like sales tax exemptions and a strong net metering program, making solar installations more attractive to homeowners.
2. Texas
Texas, known for its oil and gas industry, is also making significant strides in solar energy. The state’s large size and high electricity consumption make it an ideal candidate for solar power. Texas offers various incentives, such as property tax exemptions and net metering, encouraging homeowners to invest in solar energy.
1. California
California is the undeniable leader in residential solar energy. With abundant sunshine and progressive energy policies, the state has more installed solar capacity than any other. California’s solar initiatives, including the California Solar Initiative (CSI) and net metering policies, have made solar power accessible and affordable for many homeowners.
Conclusion
These ten states are leading the charge in residential solar adoption in the United States. Their success can be attributed to a combination of favorable climates, supportive policies, and financial incentives. As more homeowners recognize the benefits of solar energy, it’s likely that other states will follow suit, accelerating the transition to a more sustainable and renewable energy future.
The US power grid began serving consumers in the late 19th century and was a major factor in the fast economic uprising of the nation. Despite the fact that most people use the power grid, few understand how it works, much less the modern complications of its operation.
As more people make the switch to renewable energy, they can expect shifts in the very systems that impact their electricity use. In order to understand how these changes affect one another, one must trace its history back to its origins in Thomas Edison’s Pearl Street Station in lower Manhattan in 1882.
The History of the US Power Grid
The electric grid is as much a fixture of US history as the signing of the Declaration of Independence. The first recorded electric distribution systems date back to 1882 in New Jersey and Manhattan. They used direct currents across copper wires.
Historians credit Thomas Edison with creating more efficient generators to replace those used in this system. By 1907, Edison would become the first person to merge power services into a single company. Thus, the single US power grid was conceived.
From that point on, power grid expansion grew at a rapid pace. By the end of 1969, the US had over 60,000 circuit miles of power lines across the nation. But as energy sources diversify and progress, more people question whether the US power grid is the most efficient delivery system.
How the US Power Grid Works
The power grid accounts for up to 60% of the power in the US. The process of creating power and sending it to citizens happens in three steps.
Step 1: Generation
Many people are aware of natural electricity like static and lightning. But, the energy we use every day doesn’t come from thin air like those examples. Instead, electricity goes through a generation process.
Generation happens at power plants. The U.S. Energy Information Administration reports that there were over 11,000 power plants in the US at the beginning of 2021.
Power plants house electric generators that convert fossil fuels (like coal or oil) into usable electricity. The use of these fuels opens the power grid up to criticism at its very conception. Environmentalists attest that, as a limited resource, using fossil fuels is inherently unsustainable.
Step 2: Transmission
Think of transmission as large-scale distribution. Using long-distance power lines, massive amounts of electricity travel along the power grid to different regions. Electricity flows through these lines in two ways.
Alternating current (AC) lines change the electromagnetic fields of the voltage and current as it travels. Direct current (DC) lines carry a constant voltage and current without changing electromagnetic fields. AC is preferable within the power grid because it’s able to transform electricity at higher voltages.
Step 3: Distribution
The power lines in your neighborhood are part of the US power grid distribution system. They localize and distribute power from the regional level to each building- including your home.
Is This an Effective System?
There are many ways in which the US power grid is efficient. The three-step process by which it functions is simple, expandable, and centralized.
However, it’s anything but unshakable. Major storms or events, like Hurricane Sandy in 2012, have a huge impact on how people get power during emergencies.
More than 8 million people couldn’t access power for days following Hurricane Sandy. The storm wiped out utilities faster than they could repair or replace equipment before it was overtaken by flood waters.
Not to mention the fact that it isn’t safe for workers to fix power lines in inclement weather. However, since electricity is an amenity people rely on to survive during emergencies, not having it can prove fatal. Solving the problem of energy delivery in crisis situations is part of why there’s so much focus on alternative energy sources like solar energy to decentralize energy distribution.
The US Power Grid: Complications and Limitations
While the US power grid has a long history in the nation, the future outlook of this system is more daunting than ever. Its failures have become more frequent in recent years.
Increased Outages
On average, each American dealt with over 8 hours of power outages in 2020. Increasing outages are an alleged result of more extreme weather patterns.
So, although the system hasn’t changed, there are more blackouts than ever before. The most obvious solution to this issue would seem to be grid modernization. For the US power grid, modernization would require moving power lines underground, making exposed lines fire-resistant, and other protections against harsh weather patterns.
So far, the Biden administration has reserved $65 billion for modernizing the US electric grid. However, the project is subject to many roadblocks. From pushback at the state level to securing permits and integrating renewable energy into the grid, it could take years to modernize.
Non-Renewable Energy
We’ve already briefly touched on the unsustainability of the US power grid since it relies on fossil fuels. Amid America’s growing concern for the environment, more people are searching for sustainable solutions. This includes decentralizing their energy consumption using renewable energy.
Renewable energy threatens the viability of the US power grid. Even though many renewable energy users still use grid lines to power their homes, a process called net metering means they don’t pay back into the grid. With net metering, power companies must buy unused electricity back from solar energy users each month at the full rate.
While net metering encourages making the environmentally-friendly choice, it’s a financial detriment to the existing grid. As people take their power supply into their own hands, less money goes to power companies.
One way to offset this is to integrate renewable energy into grid modernization. In that way, the grid will empower people to make eco-conscious choices using it.
Alternative Energy and the US Power Grid
When people think about renewable energy in their homes, the first thing that comes to mind is rooftop solar panels. They imagine their roofs topped with large, black panels that soak up the sun and power their homes. Though popular, solar panels are but one renewable energy option for homes.
However, there are other sustainable energy integrations available. Other options include wind and hydroelectricity. Moreover, you can look into hybrid systems, such as supplementing your wind electric system with a solar battery.
When integrating renewable energy into a home or business, you have two options. The first is to connect your system to the existing grid. The second is to take it off grid. Each option has its pros and cons.
Connecting Renewable Energy to the Grid
Renewable power sources connected to the grid have a myriad of perks- the first of which is net metering. If you’re producing more electricity than you’re using, the grid diverts that power to other places. But, at the end of the month, you get paid for providing that electricity.
Moreover, you still have access to grid-generated power. That means that if your renewable power sources run out, you won’t lose access to electricity.
But, connecting your renewable energy system to the grid has its drawbacks. For example, you’ll still experience blackouts when power lines go down during extreme weather or when routine maintenance happens. That is unless you have a backup battery or generator handy.
Going Off Grid
The main perk of going off grid with renewable energy is decentralized power. The energy produced by your system is yours alone.
Of course, these systems are also susceptible to harsh weather. However, you have more control over their maintenance and repair. So, a downed pole two neighborhoods away won’t impact your access to electricity.
The downside to all off grid renewable energy options is that they are often out of your control. Even with battery storage, long stints of overcast weather can cause homes that rely on solar to lose electricity. The same goes for wind and hydropower which rely on the weather to generate energy.
Finally, depending on your power provider, you may not have a choice in whether you connect or go off grid. Your power provider will be able to tell or direct you to their requirements for renewable energy.
Will Off Grid Renewable Energy Power my Home?
One question many consumers face is whether off grid renewable energy will be enough to power their entire home. The answer to this question relies on many factors including:
- The size of your home
- How often you’re at home using electricity
- What do you use electricity for
- The abundance of renewable resources (sunshine, wind, running water)
Depending on your location, you may not be able to power an entire home on renewable energy alone. But that doesn’t mean you should give up on using it- just supplement your renewable energy with the US power grid.
How Many Solar Panels to Power a House Off Grid?
Off grid solar installation should consider your energy uses and sunlight availability at your location. Solar installers will help you figure out how much solar panel space you’ll need based on your average monthly usage and climate.
But as a general rule of thumb, experts recommend 5 kilowatts (kW) for every 1,000 square feet. Depending on the wattage you choose for each panel, that equals 15-18 solar panels for a 1,000-square-foot home.
Interested in Alternative Energy?
The US power grid is a centuries-old system in desperate need of modernization. But, with roadblocks and red tape, it’s impossible to guess just how soon that will come. In the meantime, alternative energy is the best way for consumers to empower themselves.
LGCY Power is a leading solar company that services businesses, nonprofits, government buildings, agriculture, and residential. To learn more about going solar or to get a solar installation quote from one of our licensed and experienced electricians, contact us today.
There’s a lot of buzz around solar panels lately and for good reason! These panels have a ton of benefits, from reducing your carbon dioxide footprint to saving you money on your energy bill.
But many people don’t know how solar panels are made. In fact, many people believe that they can create efficient solar panels in their own garage for little cost and no risk. This can be quite problematic and result in serious expenses if problems occur.
In this guide, we will walk you through the entire process of how are solar panels made. You’ll learn about the different types of solar panels, how they’re manufactured, and the benefits of going solar.
Keep reading to discover the wonders of the solar system and how it can be utilized to provide clean energy for all.
Solar Panels: A Brief History
Solar panels have been around for centuries, but they’ve only become widely used in the last few decades. Solar panel manufacturers started becoming more commonplace.
The first modern solar panel was created in 1954 by Bell Labs. This panel was made of silicon, which is still used in many solar panels today. Solar panels were originally used for powering spacecraft and satellites.
But as technology improved, solar panels became smaller and more efficient. In 1977, the first residential solar panel system was installed in California. And since then, the use of solar panels has grown exponentially.
How Are Solar Panels Made?
Solar panels are made up of several different components, including an inverter, a charge controller, and batteries.
The most important part of a solar panel is the photovoltaic cells. These cells are made of silicon and they convert sunlight into electricity. The pv cells are connected together to form a solar panel.
Solar panels are manufactured in a cleanroom environment. This is because the slightest bit of dust can contaminate the photovoltaic cells.
The cells are placed on a metal sheet and cut into small squares. They are then placed in an oven and heated to high temperatures. This process removes any impurities from the silicon.
After the solar panels are cooled, they undergo a series of tests to ensure that they meet quality standards. Once they pass these tests, the solar panels are ready to be installed!
Why Go Solar?
There are many reasons why you should consider going solar. Solar energy is a renewable resource, which means it will never run out.
It’s also much cleaner than other forms of energy, like coal and natural gas. Solar panels have a small carbon footprint and they don’t produce any air pollution.
Another great reason to go solar is that it can save you money! Solar panels can reduce your electricity bill by up to 50%.
And in some cases, you may even be eligible for government incentives. Going solar is a great way to save money and help the environment at the same time!
The List of Benefits of Solar Power is Long
We’ve only scratched the surface of all the benefits of solar energy. Solar power is becoming more and more popular and for good reason! These panels are environmentally friendly and cost-effective, and they have a bright future ahead.
Here are some of the other benefits that solar power provides:
- Solar energy is free once you’ve installed the initial panels
- Solar panels have a very long lifespan (25-30 years)
- Solar power is becoming more efficient as technology improves
- Solar panels can be used to generate electricity, heat water, and more
As you can see, there are many reasons to consider going solar. Solar panels are an investment that will pay off for years to come.
What Are Solar Panels Made Of?
Solar panels are made of several different materials, including glass, aluminum, and pure silicon. The most important part of a solar panel is the photovoltaic cells. These silicon cells are made of silicon and they convert sunlight into electricity.
Furthermore, solar panels also contain an inverter, a charge controller, and batteries. These components work together to store the energy generated by the solar panel so that it can be used at a later time.
In greater detail, these parts are made as follows:
The solar cells are cut from silicon wafers, which are thin layer slices of crystalline silicon. It is a single crystal element.
The aluminum frame is made from extruded aluminum, which is heated and passed through a die to create the desired shape.
The glass cover is made from tempered glass, which is heat-treated to make it stronger. It often come with an anti reflective coating.
What Are the Materials Used to Make Solar Panel Components?
The primary component is the silicon as mentioned prior. This material is sourced by mining quartzite and processing it with heat to create silicon tetrachloride.
This chloride is then reacted with hydrogen to create trichlorosilane. This substance is then reduced with hydrogen to finally produce the monocrystalline silicon used in solar cells.
Aluminum, glass, and other metals make up the rest of the panel. The aluminum is sourced from bauxite ore which is refined into alumina before being smelted to create aluminum alloys used in frames.
The tempered glass is made by heating common float glass until it reaches its softening point and then rapidly cooling it to strengthen it.
Some other materials are made/sourced by the following processes:
Indium tin oxide (ITO) is deposited on the glass through sputtering, which is a process where the material is ejected from a target and onto a substrate.
The back sheet is made of polyvinyl fluoride (PVF), which is produced by fluorinating vinyl chloride.
Ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) encapsulant material is made by combining ethylene and vinyl acetate monomers.
What Would It Take/How Difficult Would It Be to Make Your Own Solar Panel?
The solar cell is the most important and difficult part to make. To create a silicon wafer, quartzite must be mined and then heated to extremely high temperatures. This process requires specialized equipment that most people do not have access to.
Even if you were able to obtain the necessary materials and equipment, it would be very difficult to create a solar panel that is as efficient as those that are commercially available.
Solar panels are typically only around 15% efficient, which means that only 15% of the sunlight that hits the panel is converted into electricity.
Commercially available solar panels are made in large factories with expensive equipment. The manufacturing process is also heavily automated, which further reduces the cost of production. For these reasons, it is not realistic for most people to make their own solar panels.
The Positive Impact of Solar Panel Installation: Saved Trees, Better Air, Renewable Energy
Solar panels have a positive impact on the environment in several ways. First, they save trees.
Solar panels require far less land than other forms of energy generation, such as coal or natural gas. In fact, if solar panels were used instead of Fossil fuels, we could save up to 50 million acres of land by 2030.
Second, solar panels help improve air quality. Solar installations do not produce emissions, which means that they can help reduce smog and other pollutants in the atmosphere.
Finally, solar energy is a renewable resource. Unlike fossil fuels, which will eventually run out, there is no limit to the amount of sunlight that we can harness for energy. This makes solar an excellent long-term solution.
Solar Panel Installation Advice & Guidelines
Now that you know how solar panels are made, you may be wondering if solar is right for your home or business. The first step is to determine whether your property receives enough sunlight to make solar a viable option.
If you live in an area with long winters and short summers, it is likely that your property does not receive enough sunlight to justify the cost of installation. However, if you live in a sunny climate, solar may be a good option for you.
Another factor to consider is the size of your roof. Solar panel installations require a large amount of space, so properties with small roofs may not be suitable candidates.
Finally, you will need to decide whether you want to install the panels yourself or hire a professional. Solar panel installation is a complex process, so it is generally best to hire a professional if you are not experienced in this area.
If you are considering solar panel installation, be sure to follow these guidelines to ensure that the process goes smoothly.
Common Mistakes Made With DIY Solar Panel Installation
Although solar panel installation is a complex process, it is possible to do it yourself if you are experienced in this area. However, there are some common mistakes that people make when they try to install solar panels on their own.
One of the most common mistakes is not properly preparing the surface of the roof.
Solar panels must be installed on a flat, level surface in order to function correctly. If the surface of your roof is not prepared properly, the panels will not work as efficiently as they could.
Another mistake that people make is not securing the panels correctly. Solar panels are very heavy and can easily be damaged by high winds. In order to prevent this from happening, it is important to secure the panels with brackets or straps.
Finally, people often underestimate the amount of work that is involved in solar panel installation. This process is very time-consuming and requires a great deal of patience. If you are not prepared for this, it is likely that you will make mistakes.
If you are considering solar panel installation, be sure to avoid these common mistakes. With proper preparation and care, you can successfully install solar panels on your own.
Should You Hire a Specialist to Source, Install & Maintain Your Solar Panels?
When it comes to solar panel installation, you have two main options: you can either do it yourself or hire a professional. If you are experienced in this area, then you may be able to successfully install the panels yourself. However, there are several disadvantages to this approach.
First of all, it is important to remember that solar panel installation is a complex process. If you make even a small mistake, it could result in the panels not working correctly. This could waste a lot of money and time.
Secondly, sourcing and installing solar panels is very labor-intensive. It is likely that you will need to take time off work in order to complete the project. This could end up costing you more money in lost wages than you would save by doing the work yourself.
Finally, you will need to maintain the solar panels on a regular basis. This includes cleaning them and checking that they are working correctly. If you do not have the time or expertise to do this, then it is best to hire a professional.
If you are considering solar panel installation, weigh up the pros and cons of doing it yourself before making a decision. Hiring a professional may cost more money upfront, but it could save you money in the long run.
Solar Energy for You
There are many factors to consider when deciding whether or not to install solar modules. However, if you do your research and prepare properly, solar panel installation can be a great way to save money and energy.
If you are unsure about installing the panels yourself, hire a professional to do it for you.
They will have the experience and expertise to ensure that the job is done correctly. Ultimately, solar clean energy is a great choice for anyone looking for an environmentally-friendly and cost-effective way to power their home.
Now that you know how are solar panels made, if you’re interested in learning more or finding the right solar panel for your needs, get in touch with us and we will assist you in this regard.
Are you thinking of making the switch to solar but are worried about losing power on cloudy days? Don’t worry because today, we’ll be separating fact from fiction when it comes to solar panels and less-than-ideal weather conditions so you can make a truly informed decision.
Let’s dive right in!
Do solar panels work on cloudy days: the short answer
There’s no need to worry because yes, most photovoltaic solar panels do work on cloudy days because they’re designed to generate power using both direct and indirect sunlight.
This, however, doesn’t mean they work as well as they do on sunny days. In fact, depending on the amount of cloud coverage, your solar panels could drop to as low as 10 to 25% capacity, which could mean insufficient power for your home, depending on how long the situation lasts.
But we’ll get to that later. Let’s first go over three other situations that may negatively affect your solar power system’s performance.
Situation 1: Rainy days
For the most part, the result would be the same. Since the sun doesn’t really “go away” on rainy days, your solar panels should still get some indirect sunlight to work with. This means while you do need to deal with lower levels of energy production, you don’t really have to worry about it ever dropping to zero.
And rainy days aren’t totally bad for solar energy systems either. Rainfall can actually wash away dirt and debris build up from solar panels, allowing them to work better on sunny days.
And with that said, let’s move on to the second situation.
Situation 2: Snowy days
At first glance, rainy and snowy days shouldn’t be all that different because there’s still some indirect sunlight available in both situations. However, the similarities stop there.
You see, unlike rain, which simply rolls off your solar panels, taking dirt and debris with it, snow actually ends up covering them, further reducing their ability to produce power for your home.
And even after it stops snowing, the snow already covering your solar panels would still be there until it melts. To make matters worse, it can also act as glue for dirt and debris, which can get left behind when it finally melts off. So, to make sure your solar panels are able to work at peak capacity during winter, always make sure it’s not covered in snow, dirt, and debris for extended periods of time.
But even on sunny days, it’s important to regularly clean your panels to prevent dirt and debris build up.
Situation 3: Nighttime
Unlike rainy days, which can actually be beneficial to your solar system, nighttime renders it completely useless—unless you implement the measures we’ll show you later.
As we’ve established earlier, solar panels are only able to produce power when there’s either direct or indirect sunlight available, which obviously isn’t the case at night.
There’s no need to worry, though. Again, there are measures you can take to ensure you have enough power to last through the night.
Option 1: Solar batteries
On sunny days, your solar power system tends to produce more energy than your household needs during peak sunlight hours. If you invest in solar batteries, you’ll be able to store this excess power for use either at night or during periods of decreased solar system performance.
This ultimately allows you to enjoy a steady supply of clean, affordable energy throughout the year despite changing seasons and weather conditions.
The only downside is that this benefit comes at a cost—literally—because you’ll have to purchase your batteries as an add-on to your solar energy system. In addition, you’ll also need to make sure you have enough extra space in your home to house them.
At the end of the day, it’s up to you to decide whether the convenience and peace of mind are worth the extra investment. But keep in mind that without solar batteries, you’ll need to buy power from the utility company whenever your solar power system isn’t producing enough energy (or at all), which also costs money.
Of course, you can always just consult a solar specialist to ensure you get the best setup for your specific needs based on your budget.
Option 2: Net metering
Simply put, net metering is an agreement with your utility company where you get to sell them any excess power your solar system produces in exchange for incentives such as rebates and credits.
You can use these incentives to offset—either partially or completely—the cost of buying power from the utility company during times of suboptimal solar power system performance.
However, while net metering is definitely a great alternative to purchasing solar batteries, especially if you have a limited budget, limited space at home, or both, it’s not yet available in all states. Make sure you check your local regulations first before making your decision.
What if net metering is not available in your area and you can’t afford solar batteries?
Even if net metering is not available where you live and it’s not financially feasible for you to purchase solar batteries, you still don’t actually have to worry about power outages at night or during less-than-ideal weather conditions.
First, if you stay connected to the grid after you have your solar system installed, your home will simply automatically switch to using power from it whenever your system fails to supply the amount you need.
Sure, without net metering, you’ll have to pay full price to the utility company whenever this happens, but it’s still a great way to ensure you won’t ever have to worry about only having power during sunny days.
Besides, the total amount you’ll be spending on electricity per year would still be lower compared to if you didn’t have your solar energy system.
Second, you can always just finance your solar power system purchase—including the solar batteries—so you don’t have to shell out as much cash up front (if at all). Let’s go over this in more detail in the next section.
Financing your solar power system purchase
When it comes to financing your solar system purchase, you have three primary options: a solar loan, a solar lease, and a solar PPA.
Let’s take a closer look at each one:
- A solar loan, as you may have guessed by the name, allows you to purchase a solar power system without paying for it up front. Instead, you pay a much smaller fee per month until you pay the total cost off.
By the way, if you ever decide to get your solar loan through LGCY Power, you’ll get access to benefits such as:
- Monthly payments lower than your energy bill
- System maintenance support
- Product and workmanship warranty
- Federal solar tax credit and other government incentives
- The second way to make acquiring a solar power system for your home easier on the budget is by getting a solar lease. It works practically the same way as a solar loan. The only difference is that you don’t actually get to own the system if you choose this option.
The benefits you get to enjoy in case you decide to get one through LGCY Power are exactly the same as well.
- The third option you have for making switching to solar more financially feasible is by signing a solar PPA (power purchase agreement). In this setup, the solar company retains ownership of the solar system and simply charges you for the amount of power you use.
It’s just like how you’re paying your utility company for electricity right now. The only difference is it costs significantly less and it uses a much cleaner and more sustainable resource to power your home.
Can high-efficiency solar panels make up for unfavorable weather conditions?
The short answer is probably not—unless you specifically account for the occasional performance drops when choosing a solar energy system for your home.
The problem with this approach is that you’ll be spending so much more money on a system that will produce significantly more energy than you need on sunny days—which you have no way of storing or earning from if you didn’t have solar batteries or a net metering agreement with your utility company.
But if you did have solar batteries and a net metering agreement in place, then you wouldn’t really need to account for performance drops in the first place.
Besides, even if you had the most efficient panels around, they still wouldn’t work at night anyway.
The bottom line
Even on cloudy, rainy, or snowy days, as long as there’s direct or indirect sunlight available, your solar energy system should still be able to produce power for your home, albeit at a lower capacity.
The only time solar panels actually stop working is at night when there’s absolutely no sunlight to work with—but this does not mean you have to bear with not having power every time the sun goes down.
You can ensure a steady supply of power all day every day by investing in solar batteries, signing up for net metering, or doing both.
Your next steps
Book a no-obligation free consultation with one of our solar panel consultants today so we can help you find (and install) the perfect solar power system for your home—and ensure you have access to clean, affordable power, year round.











 100% Free to use, 100% online
100% Free to use, 100% online 50,000 people have chosen LGCY
50,000 people have chosen LGCY Energy advisors ready to help
Energy advisors ready to help