Considering solar panels for your home? You’re making a great decision!
Solar energy is a popular energy option, and with good reason–it’s a sustainable way to power your home. Not to mention, it can save you money in the long run.
With so many types of solar panels on the market these days, how do you know which one is right for you? We’ve got all the information you need to make an informed decision about your home’s energy future.
Solar Panel Definition
Solar panels are devices that convert sunlight into electricity. They are typically made from a silicon solar cell, which creates an electrical current when exposed to light.
There are many uses for solar panels, including powering homes and businesses, charging batteries, and providing power for small electronic devices. They are becoming increasingly popular as renewable energy sources, as they do not produce greenhouse gases or other pollutants.
How Do Solar Panels Work?
Solar panels are devices that convert sunlight into electricity. They’re made up of a series of solar cells called photovoltaic cells connected with semiconducting material.
When the sun shines on the solar cells, they create an electrical current. This current is then sent to an inverter, which converts it from direct current (DC) to alternating current (AC). AC is the type of electricity that’s used in your home.
Solar panels are usually mounted on the roof of a home, although some homeowners install them on the ground. The angle at which they’re mounted will affect how much sunlight they receive and, as a result, how much electricity they produce.
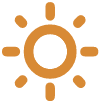
Types of Solar Panels
There are two solar panel types: crystalline and thin-film. Both have their advantages and disadvantages, which we’ll go into more detail about below.
Crystalline solar panels are made of silicon, a very common element on Earth. In fact, it’s the same material used to make computer chips. They’re the most popular solar panel on the market and come in two types: monocrystalline and polycrystalline.
Thin-film solar panels are made of a thin layer of photovoltaic material of cadmium telluride (CdTe), copper indium gallium selenide (CIGS), or amorphous silicon (a-Si) deposited on a substrate. Thin-film solar panels are the least efficient type of solar panel, but they’re also the lightest, most flexible, and most affordable.
Monocrystalline Solar Panels
Monocrystalline solar panels were invented in 1954, though solar energy using selenium was produced much earlier. Ten years later, NASA took solar power to space. But solar panels didn’t become popular until 1973 when the infamous oil embargo forced people to look at their energy usage closely.
The first solar-powered building, Solar One, was built by the University of Delaware in 1973. By 1974, the federal government began taking a serious look at the role solar power could play in conserving energy. However, it wasn’t until 2001 that Home Depot started selling solar panels for residential use.
Monocrystalline solar panels are made of a single, large crystal of silicon that is cut into thin wafers and connected to create a solar cell. They’re typically black and the most efficient type of solar panel available today.
Advantages
- They can convert more sunlight into electricity than any other type of solar panel.
- They have a long lifespan – typically around 25 years
- They perform well in high-temperature conditions
- Made of high-grade silicon
- Requires less space than other types of solar panels
- Lifespan of 35-40 years
- Recyclable
Disadvantages
- They’re the most expensive type of solar panel
- They require more space than other types of solar panels
- Snow and debris can cause a circuit failure
- Not well-suited for cold weather conditions
Monocrystalline solar panels are a great option if you have a small roof or want to maximize your energy production. However, they also have a higher price tag than other solar panels.
Polycrystalline Solar Panels
The first polycrystalline solar panels hit the market in 1981. Also called “multicrystalline” solar panels, they are similar to monocrystalline solar panels in that they both use silicon crystals. The difference is that they contain multiple smaller silicon crystals instead of just one large silicon crystal.
Solar panel manufacturers make polycrystalline solar cells by melting down large chunks of silicon and then cooling them to form small crystals. These tiny crystals are then connected to create a solar cell.
Polycrystalline solar panels are typically blue or black and are less efficient than monocrystalline solar panels. That means they can convert less sunlight into electricity.
Advantages
- They’re less expensive than monocrystalline solar panels
- They function well in cooler climates
- They produce less waste during manufacturing, making them more eco-friendly.
- Lifespan of 20-35 years
- Recyclable
Disadvantages
- They’re less efficient than monocrystalline solar panels
- They require more space than other types of solar panels
- They aren’t as attractive as other solar panels
- They degrade faster than m solar panels
Polycrystalline solar panels are a great option if you’re looking for an affordable crystalline solar panel. However, they’re not as efficient as monocrystalline solar panels and take up more space, so they may not be the best option if you have a small roof.
Polycrystalline solar panels are a good option if you have a large roof and want to save money on your purchase of solar panels.
Thin-Film Solar Panels
Thin-film solar panels are made of layers of photovoltaic material placed on top of one another. There are three types of thin-film solar panels: Cadmium telluride (CdTe), Copper Indium Gallium Selenide (CIGS), and amorphous solar panels (a-Si).
CdTe Solar Panels
CdTe solar panels arrived on the scene in 1972 and boasted a 6% efficiency rate. They are much more efficient now at 19% efficiency.
CdTe solar panels make use of a thin layer of cadmium telluride deposited on a substrate. They’re the most common type of thin-film solar panel and are quick and easy to manufacture. The layer is typically made with glass or metal and connected to electrical contacts, generating an electrical flow.
CIGS Solar Panels
CIGS solar energy was discovered in 1981 by Boeing. Its efficiency was 9.4%. Now, however, it is 17.1% efficient.
With CIGS solar panels, a thin layer of CIGS gets deposited on a glass or metal substrate. The CIGS are then connected to electrical contacts, which allow for the flow of electricity. They’re the second most common type of thin-film solar panel and are highly flexible, making them a great option if you have a unique rooftop.
The a-Si is the least common type of thin-film solar panel. They are made of a thin layer of amorphous silicon deposited on a glass or metal substrate. They’re the least efficient type of solar panel available.
Advantages
- They have a long lifespan
- They’re the lightest type of solar panel
- They’re flexible
- They are visually appealing
Disadvantages
- They’re the least efficient type of solar panel
- They require a lot of space
- They have a shorter lifespan than monocrystalline and polycrystalline solar panels.
If you have a large roof or want to install solar panels on a curved surface, thin-film solar panels are a good option. They’re also a good choice if you live in an area with a lot of cloud cover, as they’re less affected by shadows than monocrystalline and polycrystalline solar panels.
Are Solar Panels Right for Your Home?
Now that you know the types of solar energy available, it’s time to decide if solar is suitable for your home. Here are some things to consider:
- The sunlight your home receives: Solar panels need direct sunlight to work effectively. If your home is in a shady area, solar panels may not be the best option.
- The size of your roof: Solar panels take up a lot of space. If you have a small roof, you may be unable to fit enough solar panels to power your home.
- The type of roof you have: You can install solar panels on most types of roofs. Even tiled roofs support solar panels.
- Your energy needs: Solar panels are most effective when supplementing your existing energy sources. If you have a high energy need, solar panels may not be able to meet all of your needs.
- Your budget: Solar panels can be expensive. They may not be the best option if you’re on a tight budget.
If you’re unsure what solar module is right for your home, we recommend speaking to a solar panel expert. They can help you assess your needs and find the best option for your home.
What Are the Best Solar Panels for Your Home?
The best solar panels for your home depend on a few factors, including your budget, the size of your roof, and the amount of sunlight your home receives.
A monocrystalline solar panel system is perfect if you want to maximize energy production. A polycrystalline solar panel system is an excellent option if you have the space and want to save money on your solar panel purchase.
Monocrystalline vs. Polycrystalline
If you’re trying to decide between monocrystalline and polycrystalline solar panels, the most important factor to consider is their efficiency. Monocrystalline is more expensive than polycrystalline, but is also more efficient.
Solar panel efficiency refers to the amount of electricity generated from sunlight absorbed by the panel. So, the higher the efficiency, the more electricity the solar panel produces. Monocrystalline solar panels have an efficiency of 15-22%, while polycrystalline solar panels have an efficiency of 13-17%.
Monocrystalline solar panels are a great choice for small roofs, as they’ll produce more electricity. If you have a large roof, you might choose polycrystalline solar panels as they’re less expensive and will still make a significant amount of electricity.
Thin-Film vs. Monocrystalline and Polycrystalline
If your climate experiences a lot of rain and cloudy conditions, thin-film solar panels may be your best option. Thin-film solar panels are less affected by shadows than monocrystalline and polycrystalline solar panels, as they have a lower light absorption coefficient.
The light absorption coefficient is the amount of sunlight absorbed by the solar panel. The higher the light absorption coefficient, the more sunlight is absorbed, and the lower the electricity production. Thin-film solar panels have a light absorption coefficient of 5-15%, while monocrystalline and polycrystalline solar panels have a 20-25% light absorption coefficient.
Choose thin-film solar panels if you have a large roof, a small budget, and experience less sunlight than other areas. However, you will be trading efficiency and durability for convenience.
Solar Panel Efficiency
Solar panel efficiency measures the amount of sunlight that’s converted into electricity. The higher the efficiency, the more electricity a solar panel can produce.
Monocrystalline solar panels are the most efficient type of solar panel, with an average efficiency of 20%, whereas polycrystalline solar panels aren’t quite as efficient. Even so, they still have an average efficiency of 15%. Thin-film solar panels have an average efficiency of 12%.
Solar Panel Size
Solar panel size is measured in watts. The higher the wattage, the larger the solar panel. Solar panels range in size from 50 watts to 400 watts.
The average home uses roughly 940 kilowatt-hours (kWh) of electricity per month. To put this into perspective, a 100-watt solar panel can produce about 8 kWh of electricity per month; and a 400-watt solar panel can produce about 32 kWh of electricity per month.
Which Ones Are Most Attractive?
The most attractive solar panels are those that blend in with your roof. Monocrystalline solar panels are the most visually appealing type of solar panel, as they’re typically all one color. Polycrystalline solar panels are also attractive, as they have a mottled appearance. Thin-film is the least attractive type of solar panel, as they’re typically blue or black.
If you want your solar panels to be as unobtrusive as possible, thin-film solar panels are the best option. However, if you don’t mind your solar panels being visible, both monocrystalline and polycrystalline solar panels are good options.
Still not sure? Type “solar panel pictures” into your web browser for a quick look at different solar panel images. Doing this will give you an idea of each type of solar panel.
Solar Panel Warranties
Most solar panels have a 25-year warranty to protect against defects and performance deterioration.
Some manufacturers offer extended warranties for an additional cost.
Solar Panel Maintenance
Solar panels require very little maintenance. It’s best to clean your panels every few months to remove dirt, dust, and leaves. You can clean your panels with a hose, a brush, or a sponge.
You should also check your panels regularly for signs of damage, such as cracks or scratches.
Can Solar Panels be Recycled?
The short answer is yes, solar panels can be recycled. In fact, most solar panels are made with materials that can be reused or recycled.
The recycling process starts by crushing the solar panels into small pieces. Then, the pieces are cleaned and smelted down to extract the materials. Finally, the materials are separated and melted down again to create new solar panels.
Solar panels can be recycled over and over again, making them a very sustainable product. And, recycling solar panels helps to reduce the amount of waste that goes into landfills. So, not only are solar panels good for the environment, but recycling them is good for the environment too.
Solar Plus Storage
Solar plus storage is a system that includes solar panels and a battery. Solar plus storage systems allow you to store energy from the sun for use at night or during a power outage.
Solar plus storage systems are more expensive than traditional solar panel systems, but offer peace of mind and energy savings. They are becoming more popular as battery technology improves and the cost of batteries decreases.
Things to Consider Before Purchasing Solar Panels
Before investing in solar panels, you should consider a few things. First, you need to determine how much electricity you need to produce. Knowing how much electricity you use will help you determine the size of the system you need.
You need to consider the installation cost and compare it to the cost of buying electricity from your utility company. To help offset the price, state and local governments offer incentives for purchasing and using solar panels.
Solar panels may not be the most suitable option for your home in certain instances due to age or tree cover. If there are trees near your property that shade your roof excessively, rooftop solar systems may not be the best choice.
The size, form, and slope of your roof are also factors to consider. Solar panels perform best on roofs with a slope of 15 to 40 degrees, although other roofs may also work.
You should also consider how soon you will need to replace your roof. If you need to replace your roof relatively soon, it is best to hold off installing solar panels until you can do so.
Installing Solar Panels: Can I Do It Myself?
Once you’ve decided which type of solar panel is right for your home, the next step is to install them. Installing solar panels requires specialized training and equipment.
As such, it’s not something most homeowners should do themselves. A professional knows the ins and outs of solar panel installation.
If you live in an area with high electricity costs, installing solar panels may prove to be an eco-friendly way to save money. With the right solar panel system, you can produce all the electricity you need to power your home.
Incentives to Installing Solar Panels
There are many incentive programs available to encourage homeowners to install solar panels. These incentives can reduce the cost of solar panel installation by 30% or more.
The federal government offers a tax credit for solar panel installations. The tax credit is 26% of the cost of the system, up to $2,000. State and local governments also offer incentives, such as rebates and tax credits.
LGCY Power does not offer advice on accounting or tax related matters. We recommend to all of our clients that they consult with a certified tax professional.
How Will Solar Panels Impact the Resale Value of my House?
How solar panel systems impact the resale value of your home depends on several factors, such as the system’s cost, the system’s size, and the system’s age.
Solar panel systems generally increase home resale value based on the kilowatt (kW) of installed capacity.
Solar Panel Cost
Solar panel costs have fallen drastically in recent years, making them more affordable than ever. The cost of a solar panel system depends on the type of solar panels you choose, the size of your system, and the installation costs in your area. The average price of a solar panel system is varies, depending on the type of solar panel system and the state you live in.
Save Money in the Long Run
The amount of money you save by using solar panels depends on the cost of electricity in your area, the size of your system, and the amount of sunlight your home receives. Many homeowners save about 75% on their electric bill after switching to solar.
A Solar Panel System Will Eventually Pay for Itself
The payback period is the amount of time it will take for your solar panel system to pay for itself. The payback period depends on your system’s size, the electricity cost in your area, and the incentives you receive. Generally, you can expect a payback period of 7 to 12 years.
Financing Solar Panels
There are a few different options available for financing solar panels. You can pay for the system outright, take out a loan, lease the system, or use a power purchase agreement (PPA).
Cash Pay
Paying for the system outright is the best option, as you’ll save on interest payments. However, not everyone has the upfront cash to pay for a solar panel system.
Leasing and Loans
You can finance it with a loan if you don’t have the cash to pay for a solar panel system outright. Many types of loans are available, so you’ll need to compare options to find the best rate.
Leasing a solar panel system is another option. With a lease, you make monthly payments to the leasing company. The leasing company is the owner of the solar panel system and is responsible for maintenance and repairs.
At the end of the lease, you have the choice to purchase the system or renew the lease.
Power Purchase Agreement (PPA)
A PPA is a type of financing that allows you to pay for the electricity that your solar panel system produces. With a PPA, you enter into an agreement with a solar developer. The developer owns the solar panel system and is responsible for maintenance and repairs.
You agree to purchase the electricity that the system produces at a fixed rate for a set period. After the contract expires, you can renew the agreement or purchase the system outright.
Decrease Your Electric Bill With Solar Panels
Solar power is one of the fastest-growing energy sources in the world. And there’s a good reason for that. Solar energy is a renewable resource used to generate electricity, heat water, and even power entire homes and businesses.
Knowing about the different types of solar panels available is the first step to getting started with solar. Now you can start shopping for the perfect solar panel system for your home!
Making the switch to solar power has never been more accessible or affordable. At LGCY Power, we have a deep understanding of solar power and what it takes to make the switch.
We’ll work with you to develop a custom solar plan that fits your needs and budget. We’ll handle all the details, from paperwork to installation.
So if you’re ready to make the switch to solar power, fill out a simple form to receive a free estimate, or give us a call today for a free quote.