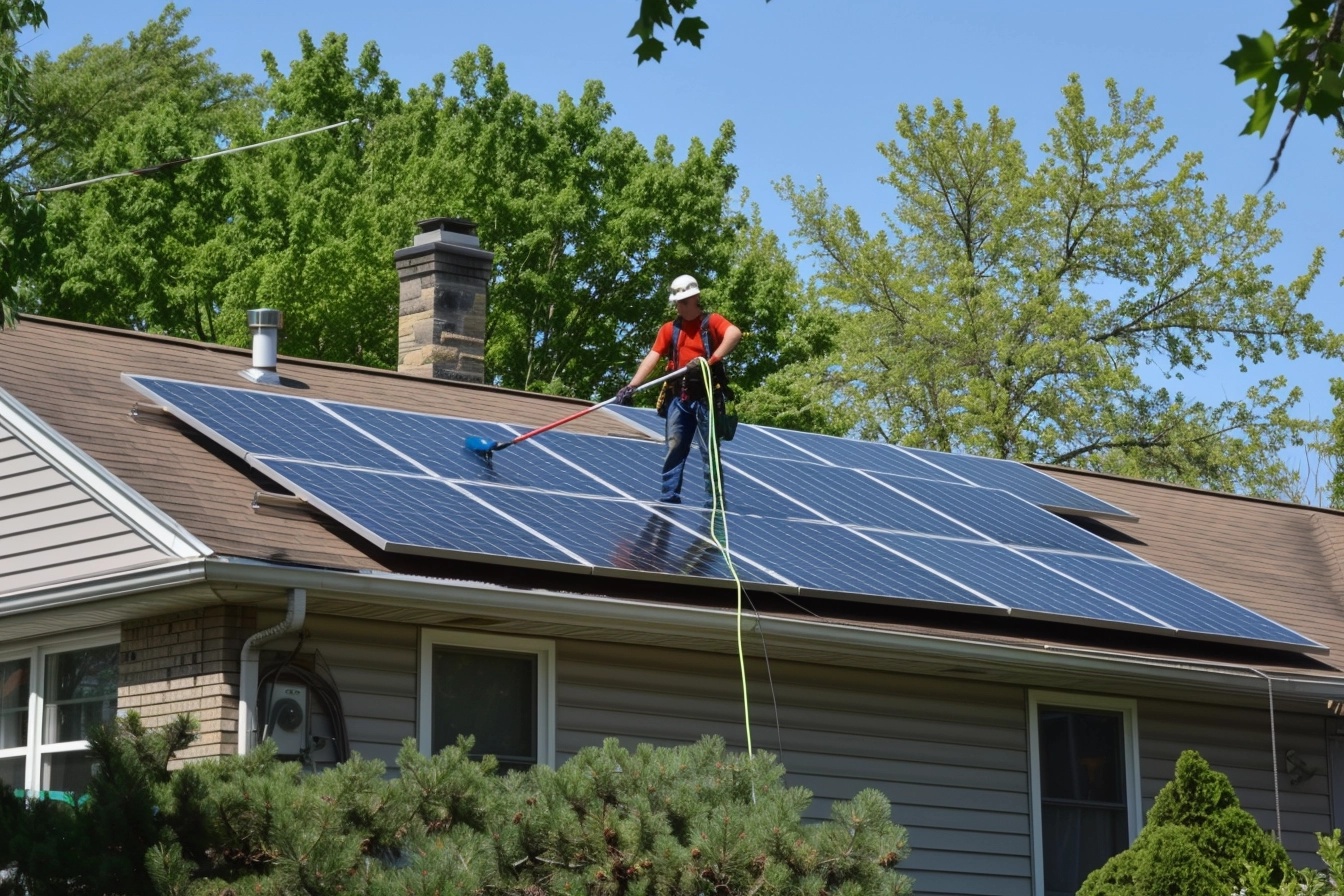
Solar panels are a great way to harness renewable energy and reduce your carbon footprint. However, to ensure they operate at peak efficiency, it’s essential to keep them clean. Dust, dirt, pollen, and bird droppings can accumulate on the panels and significantly reduce their ability to absorb sunlight. Here’s a comprehensive guide on how to clean your solar panels effectively and safely.
Step 1: Safety First
1. Turn Off the System: Before you start cleaning, make sure to turn off your solar panel system. This step is crucial to avoid any electrical hazards. Refer to your system’s manual for instructions on how to safely shut it down.
2. Check the Manufacturer’s Instructions: Consult the manufacturer’s guidelines for any specific cleaning recommendations or warnings. Some manufacturers may have specific cleaning methods or restrictions to avoid voiding the warranty.
Step 2: Gather Your Supplies
You don’t need any fancy equipment to clean solar panels. Here’s a list of basic supplies you’ll need:
- Soft brush or squeegee with a long extension
- Hose with a gentle spray nozzle
- Bucket of lukewarm water
- Mild detergent (if needed)
- Soft cloth or sponge
- Safety harness (if cleaning rooftop panels)
- Ladder (if necessary)
Step 3: Choose the Right Time
The best time to clean solar panels is either early in the morning or late in the afternoon. During these times, the panels are cooler, reducing the risk of thermal shock or damage from rapid temperature changes. Additionally, cleaning in cooler weather helps prevent the water from evaporating too quickly, which can leave streaks or residue.
Step 4: Remove Loose Debris
Start by removing any loose debris, such as leaves or twigs, from the surface of the panels. You can use a soft brush or a leaf blower for this task. Be gentle to avoid scratching the surface of the panels.
Step 5: Rinse with Water
Use a hose with a gentle spray nozzle to rinse the panels with water. This will help remove dust and loose dirt. Avoid using high-pressure water, as it can damage the panels or the wiring underneath.
Step 6: Clean with Soapy Water
Fill a bucket with lukewarm water and add a small amount of mild detergent. Dip a soft cloth or sponge into the soapy water and gently scrub the surface of the panels. Avoid using abrasive materials or harsh chemicals, as they can scratch or damage the panels.
Step 7: Rinse and Dry
After scrubbing, rinse the panels thoroughly with clean water to remove any soap residue. Use a squeegee to remove excess water and prevent streaks. If necessary, wipe the panels with a soft, dry cloth to ensure they are completely dry.
Step 8: Inspect for Damage
While cleaning, take the opportunity to inspect your solar panels for any signs of damage, such as cracks, chips, or loose connections. If you notice any issues, contact a professional for repairs to ensure your system continues to operate safely and efficiently.
Step 9: Turn the System Back On
Once the panels are clean and dry, you can turn your solar panel system back on. Refer to your system’s manual for instructions on how to safely restart it.
Additional Tips:
- Regular Maintenance: Clean your solar panels at least twice a year, or more frequently if you live in a particularly dusty or pollen-heavy area.
- Professional Cleaning: If you’re not comfortable cleaning the panels yourself or if they are difficult to access, consider hiring a professional cleaning service.
- Monitor Performance: Keep an eye on your system’s performance. If you notice a significant drop in energy production, it might be time for a cleaning or inspection.
By following these steps, you can ensure that your solar panels remain clean and efficient, maximizing their energy production and extending their lifespan. Happy cleaning!
The future of solar panels is looking very bright—literally! The cost of solar panels in the United States is decreasing, and the efficiency of solar cells is increasing. It’s no wonder that the solar industry is booming.
In fact, solar is now the fastest-growing source of clean energy in the world. There are several factors that are driving this growth.
Solar panels are also a clean and renewable source of energy. They help homeowners and businesses to reduce their carbon footprint.
So, what does the future hold for solar panels? Keep reading to find out.
Why Is Solar Power Such a Big Deal?
Solar energy is highly variable and depends on the sun’s cycles. But cloud cover and changes in weather need to be considered.
At night, solar energy cannot generate electricity. This is where supplemental energy from fossil fuels is needed. Nonetheless, the technology behind solar powered generation is improving at a remarkable rate.
Solar energy has many benefits. Here are a few:
- It decentralizes the electrical grid
- It offers a significant source of employment
- Solar-powered homes can sell their energy back to the electric grid, earning a profit
- It is a major driver of economic growth
Homeowners who install rooftop solar power systems can expect to reduce their electrical bills up to 75%. Despite the initial cost, savings will continue for the life of a solar panel system.
A Cost-Competitive Alternative to Fossil Fuel
In recent years, the cost of solar power has plummeted, making it a cost-competitive alternative to coal and other fossil fuel. Governments have also stepped up subsidies and tax breaks to encourage solar deployment. Though solar energy is not suitable in some markets, it is a viable alternative for many.
Cost estimates are constantly revised as new data becomes available. Solar PV and onshore wind have consistently exceeded initial estimates. Today, solar technologies and wind power generate over one-fifth of the world’s electricity.
Mitigate Climate Change
Solar thermal power and wind power can help us fight climate change. The warming of the planet is already leading to increased heat waves, rising sea levels, and losing sea ice. These alarming trends are projected to worsen further if significant changes aren’t implemented.
A Sustainable Source of Energy
Manufacturers make solar panels from silicon, a naturally occurring element that is abundant in the Earth’s crust. They make from materials that are recyclable, and some states have laws encouraging the reuse of these panels. These efforts are making solar power a more environmentally friendly source of energy.
The sun provides us with solar energy. As such, using solar panels for domestic use can drastically reduce your household’s power use and utility bills. Besides being environmentally friendly, solar panels are also highly durable.
Traditional electricity relies on fossil fuels. They’re not only expensive but can also be hazardous and have adverse effects on the environment. Further, fossil fuels are limited, and the prices of these sources of energy can fluctuate significantly.
Manufacturing Solar Panels
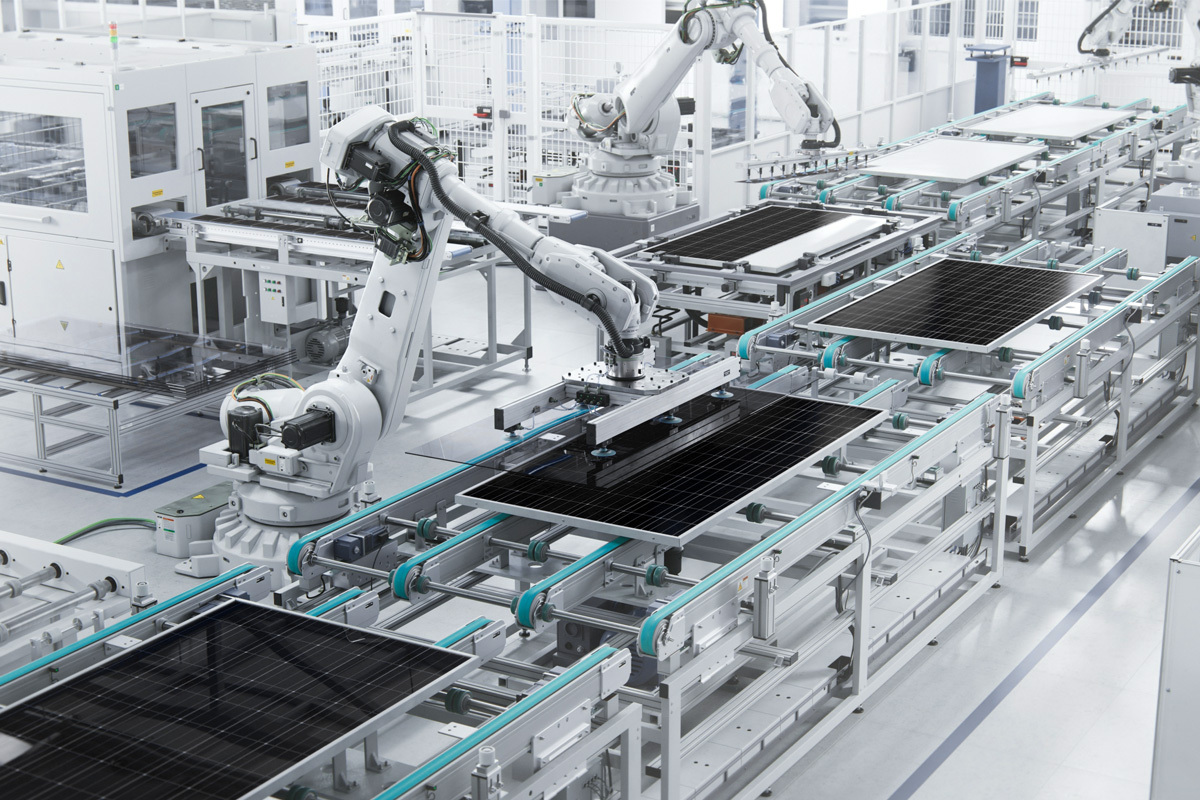
The manufacturing process for solar panels requires multiple layers and delicate components. These layers and components require precise alignment and placement. Modern factories use automated processes for cell cutting, material handling, and component bonding.
An error in any of these processes could cause a panel to perform below expectations and have a shorter operational lifespan. To ensure that solar panels meet high-quality standards, end-of-line testing is essential. Imaging can detect problems, such as cracks and misalignments.
Solar Power Potential
The sun is the most abundant source of energy. A fraction of its output provides 10 times as much energy as humans need. There’s no doubt that solar electricity generation is a rapidly growing industry.
However, its share of the overall energy market is still well below one percent. By contrast, 79% of energy consumption is derived from coal, natural gas, and oil.
Solar power has the potential to meet the world’s sustainability goals and reduce greenhouse gas emissions. Its main weakness is its inability to provide on-demand energy. Battery-based systems are expensive and environmentally harmful.
One of the most effective electricity enhancement techniques is the dual-fluid heat exchanger. This method has a greater surface area. It performs better under high operating temperatures than traditional heating and cooling methods.
Countries with limited access to electricity benefit from pico-solar systems. They are becoming a crucial component of global energy poverty relief strategies.
These systems consist of a small solar panel and a battery that powers a wide variety of appliances. Also, pico-solar systems have the potential to provide electricity to millions of people in emerging markets.
What’s In Store for Solar Energy?
The International Energy Agency is expecting solar photovoltaics to make up 13% of global electricity by 2030. This is a huge increase from the 2% it was in 2016. This rapid growth is being driven by falling costs, increasing access to financing, and improved policy support.
The report also predicts that the number of people working in the solar PV industry will increase from 2.8 million in 2016 to 8.3 million by 2030. So, what’s in store for the future of solar energy? Read on to find out!
Organic Solar Cells
Organic solar cells have many advantages over traditional photovoltaics. They are flexible, thin, and can adapt to a variety of substrates. The materials can also be tailored to absorb different wavelengths of light.
Organic solar technology has the potential for use in windows and glass facade shading, among other applications.
Organic solar cells are a relatively new technology composed of polymer molecules that have a carbon base. Made of thinly filmed plastic, organic cells are flexible and lightweight. They are also more durable than conventional solar cells.
A big advantage of using organic molecules in solar cells is manufacturers can make them with simple ingredients. In addition, they are relatively inexpensive. This allows for mass production of the material.
Organic materials can’t compete with silicon, but they can produce solar panels with similar functions.
Photovoltaic (PV) Trackers
Photovoltaic trackers can improve the efficiency of solar panels. Fixed panels can only collect significant amounts of energy when the sun is at its highest point. But a tracking system can maximize this amount over the entire day.
In addition, there are times during the year when the sun’s intensity is only about half its maximum. This misalignment can cause an energy loss of up to 20%. In these instances, photovoltaic trackers can make up for this loss with a higher output.
Photovoltaic trackers are based on the concept of a moving surface that follows the path of the sun. These devices are usually dual-axis or tip-tilt. Solar installation companies can install them on an elevated post and move with the sun.
Dual-axis trackers can generate up to 40% more energy than single-axis trackers. However, these devices are more expensive, adding three to six percent to the overall cost of a solar installation.
Photovoltaic trackers increase the amount of power produced by a solar system by coordinating its peak with the power needs of the grid. Another advantage of using a tracker is that it reduces the amount of work needed to install a large solar array.
High-accuracy solar trackers are mainly used in concentrating solar PV systems. They are also an essential component for large-scale solar installations.
These devices hold parabolic mirrors that reflect sunlight to a central collector tower containing hot liquid or gas. Using a solar tracker also enhances the efficiency of the solar panels.
Integrated Inverters
The development of inverters will benefit from IoT and Blockchain technologies. Both of these technologies can improve their diagnostic capabilities.
They will also enable the inverters to work with other core devices like cleaning robots. They’ll increase their overall plant efficiency and lifespan.
Among the many benefits of inverters, the grid-forming capability is one of the most important. This allows an inverter to auto-start a downed grid, known as a “black start.”
Inverters that use “grid-following” technology rely on an outside signal to generate a sine wave that matches the power grid. But more advanced models can also generate the signal on their own.
Inverters are an intrinsic part of solar power systems. They convert DC electricity into AC power, the type that is used by the electrical grid. The difference between DC and AC is in the energy’s voltage. DC electricity is a constant voltage, while AC power flows in both directions in a circuit.
Inverters can also help stabilize the grid and control voltage. Inverters help to feed solar power back into the grid with maximum efficiency. The quality of the PV modules and inverters is essential to the installation’s yield. There are several important factors that influence the power quality of the system.
Solar power systems have continued to improve in efficiency and output. As a result, they’ve become significantly cheaper and more portable than other energy sources. With the development of inverters and energy storage, solar is poised to become the mainstream energy solution.
eArche Solar Panels
eArche solar panels are flexible and ultra-thin, which allows them to be molded to fit any surface. They are also cheaper to produce than conventional solar panels and are easier to install. They can also power boats, trains, and motorhomes.
The team behind eArche has tested their technology, but the energy output from their tests is not large. They have only produced 0.001% of the energy produced by traditional solar panels.
In the future, they hope to develop industrial partnerships to further their research. However, there are still many unknowns. Ultimately, the future of solar power depends on future market conditions. Public policies aimed at mitigating global climate change can affect renewable energy technologies.
Anti-Solar Panels
Anti-solar panels capture the heat that leaves the earth’s surface during the night and converts it to electricity. This technology could eventually eliminate the need for batteries to store excess electricity.
Currently, the technology is only in its research phase, but it could soon be available on the market. Researchers at the University of California, Davis, are working to develop anti-solar panels. They estimate the panels could produce up to 50 watts per square meter during ideal conditions.
Anti-solar panels could be installed at industrial facilities to use the waste heat from their processes. Alternatively, they could be installed on rooftops and produce electricity 24 hours a day.
This technology would be beneficial in low-resource areas where conventional solar panels do not exist. In addition, the technology could also be combined with cooling systems that use radiative cooling to cool buildings.
Anti-solar panels use a special type of cell to produce electricity. It is very different from the photovoltaic cells found in conventional solar panels.
Instead of capturing light in the visible spectrum, anti-solar panels use mercury alloys. They are specifically designed to absorb long-wavelength light.
The technology also allows for the production of energy at night. Compared to regular solar panels, anti-solar panels can be used in both industrial and domestic settings.
Anti-solar panels provide carbon-free energy that helps reduce environmental pollution. The technology also has the potential to match solar panels in efficiency.
The concept of anti-solar panels has been around for several years, but it still hasn’t received widespread acceptance. While they are still a few years off, they are promising and could revolutionize the industry. However, there are some issues that should be addressed before they become a reality.
Solar-Powered Transportation
Developing solar vehicles remains a tough challenge. People still need transportation, especially in urban areas with tall buildings and harsh weather. Also, solar cell technology is still far from commercialization.
Some industry experts say there’s a significant gap between the theoretical and real-world use of solar vehicles. However, there are several companies working on the technology.
Another project involving solar panels is solar-powered bus stops. This is a simple but promising idea: solar panels installed at bus stops can collect energy during the day. These panels can power bus information boards and other devices.
Other solar-powered transportation initiatives include solar trains and solar scooters. A solar-powered railway train could operate on long routes at a low cost. In addition, solar e-bikes could be used for long-distance competitions. A solar e-bike race in France could end in China.
Potential Problems Solar Will Face
One of the major problems solar power will face is the issue of waste. According to the International Renewable Energy Agency, by 2050, there will be 78 million tons of waste produced annually. This is a staggering amount, but it is also an untapped billion-dollar opportunity.
This figure is based on the assumption that solar panels remain in place for the entire 30 years of their lifespan. However, it is not uncommon for homeowners and businesses to replace solar panels early.
Another potential problem is land use. Solar farms require about 3.5 to 16.5 acres of land for each MW of generating capacity. Building large solar facilities, such as these, will require fundamental changes to land use.
If the changes have negative impacts on local communities, they may cause conflict and derail solar projects altogether. Furthermore, they may fuel resistance against renewable energy development.
In addition to corrosion, solar panels can also develop moisture problems. Often, the problem starts at the edge of a panel and spreads all over it. This can result in a drastic reduction in the production of solar panels.
In fact, the darker corroded area on a solar panel is directly proportional to the reduced production of the solar panel. Moisture problems also affect glass and thin-film PV panels.
The Future of Solar Storage
The future of solar storage is highly market-dependent, and it is likely to be dynamic. Revenues at the beginning of a project may not be the same as those at the end.
In addition, the future of solar storage is highly competitive. It is competing with other energy storage technologies like standalone batteries, gas peakers, and smart EV charging.
Energy Storage
Using solar-powered batteries is a great opportunity for homeowners. Although this technology is still relatively new, a growing number of states support solar-powered batteries.
In Maryland, for example, homeowners can get a 30% tax credit for solar battery systems. This credit is good for up to $5,000 for residential and $75,000 for commercial systems. Other states, including California, offer cash rebates for energy storage systems.
A key aspect of storage technology is its ability to extend the production window of a typical solar facility. This can be very profitable in the rapidly changing power market. By enabling storage and blending it with PV, utilities can achieve a more cost-effective solution to their growing demand.
Hybrid Power Plants
Hybrid power plants with solar storage are ideal for achieving multiple benefits:
- Enhancing solar capacity factors at the access point
- Lowering costs
- Improving power output
The complementary nature of solar and wind resources means they can provide a stable supply of electricity. Additionally, they create additional revenue streams.
Hybrid plants can take advantage of battery prices’ continued decline. They are gaining in popularity among power plant developers.
Hybrid solar power plants with solar storage are becoming a reality, but there are still challenges and questions. Factors like market rules and policy incentives can make or break a hybridization project.
The authors of a new study published in The Electricity Journal examine the operational benefits, relative costs, and industry trends for hybrid power plants.
The current technology is promising. But solar manufacturers need further research to determine the best way to design and build hybrid power plants that will meet energy needs and improve the grid’s performance.
Copper
In an industry that is eager to support renewable energy, copper is one of the most promising options. The copper industry is particularly interested in benchmarking grid energy storage technologies.
Researchers expect the resulting demand for copper to range from zero to more than four tons per megawatt, depending on installation configuration, electrical equipment, and storage type. The incremental demand for copper associated with grid energy storage will range from 900 tons to over 3,000 tons.
Copper is a vital component of renewable energy systems, and it is used nearly five times more in these systems than in traditional power generation. Its excellent thermal and electrical conductivity enables copper-based electrical systems to generate and transmit energy with high efficiency and minimum environmental impact.
Dysprosium
Dysprosium is a rare earth metal that is used for a wide variety of applications. This material can store solar energy. Unlike lithium, it doesn’t have to undergo refining to be re-used.
Besides solar storage, it also has uses in electric vehicles and in permanent magnets. Some of the other rare materials used in batteries include lithium, cobalt, and neodymium.
Affordable and Accessible Solar For the Future
Costs have fallen dramatically in recent years, making solar a more viable option for a wider range of people. And as solar technology continues to improve, it will become even more accessible and efficient.
There are several factors that are driving the future of solar power. Solar is now cheaper than ever before and should continue to decrease.
Also, solar panels are becoming more efficient, meaning that more energy can be generated from a smaller amount of space. New technologies are on the way that promises even lower costs and higher efficiency. Soon, solar power will be cost-competitive with fossil fuels.
In 2010, solar energy only made up a small portion of the global energy market. It depended on subsidy schemes in countries like Italy and Germany to get off the ground. Today, however, the solar energy industry has grown significantly and is projected to surpass the combined energy production of India and China in five years.
These factors are coming together to make solar power a more viable option for the future. With continued cost reductions and improved technology, solar will become increasingly accessible and affordable for everyone.
The Future of Solar Panels Is Here
The future of solar panels is very promising. With government incentives and declining costs, solar panels are becoming increasingly popular and cost-effective. Homeowners and businesses alike are turning to solar panels to save money and reduce their carbon footprint.
To learn more about how to make solar power a part of your future, schedule a consultation with us.
- Agua Caliente Solar Park
The Agua Caliente Solar Project was built in 2011 in Yuma County, Arizona. A 290 MW facility, it was awarded the Project of the Year in the Renewable Energy Awards.

https://flic.kr/p/dib8Us
- Cestas Solar Farm
Europe’s largest solar plant, Cestas Solar Farm in France is our youngest selection on this list. It was completed in October 2015 and has a 300 MW capacity. As solar subsidies have slowed in France and other European nations, many are hoping that this is a hopeful sign of a solar-oriented future in Europe.
- Solar Energy Generating Systems [SEGS]
Solar Energy Generating Systems [SEGS] is one of the oldest and largest operating solar plants in America. It pulls power from 3 different locations and 9 total plants, totaling a MW capacity of 354 and powering 140,000 homes in the California area. SEGS is a good place to look if you are wondering how solar plants have changed with the increase in technology. Initial construction began in 1984 and was not completed until 1990, while some solar plants created now only take about 9 months to complete.
- Ivanpah Solar Power Facility
The Ivanpah Solar Power Facility (located just southwest of Las Vegas) is the largest thermal solar station in the world. It has a capacity of 392 MW and powers 80,000 homes in the Southern California area. It opened in 2014, and after a rocky start to its efficiency, it is now operation at an efficiency higher than expectation and looks to be a bright spot in the further development of thermal solar plants.
-

Matthew Dillon : https://flic.kr/p/omFSvR Copper Mountain Solar Facility
At the time, the Copper Mountain Solar Facility was a huge undertaking in the United States, as it was to be the largest photovalic solar plant in the United States. Though it has since been eclipsed, the 458 MW plant is still largely efficient, powering 89,000 homes in the California and Nevada regions.
- Huanghe Hydropower Golmud Solar Park
The Golmud Solar Park (located in the Qinghai Province in China) is one of the most acclaimed solar plants in the world. After its completion in 2011, it won the 2012 China Quality Power Project Award and was the largest solar plant in China until 2015. It has a capacity of 500 MW.
- Desert Sunlight Solar Farm
The Mohave desert has one of the highest concentration of different solar plants in the world, but Desert Sunlight Solar Farm is easily the biggest in terms of production. It has a capacity of 550 MW, while the next closest in the Mohave (which we’ll get to later) is down at 392 MW. Desert Sunlight was not completed until early 2015 despite construction beginning in 2011. After some early controversy regarding the negative impact this plant had on desert wildlife, it is now up and running and is also one of the most efficient solar plants in the world.
- Topaz Solar Farm
Upon its completion in 2013, Topaz Solar Farm was the largest solar plant in the world to date. It has been surpassed since, but it is still one of the larger and more efficient solar farms. Located in San Luis Obispo County, California and covering 9.5 square miles, Topaz has a 550 MW capacity and gives power to roughly 160,000 homes in the California area.
-

Peter Thoeny : https://flic.kr/p/wsxr6p Solar Star
Solar Star is the largest solar plant in the United States, located near Rosamond California. It is coming up on its first anniversary since being opened, as it began production in June 2015. Solar Star has a capacity for 579 MW and provides power to 255,000 homes in California.
- Longyangxia Dam Solar Park
Built in 2013, Longyangxia Solar Park is located in the Longyangxia Dam in the Qinghai Province of China. Combined with a hydroelectric power generator, the solar portion has a capacity of 850 MW, making it just shy of the largest solar plant in the world.

- Gujarat Solar Park
The largest solar plant in the world is the Gujarat Solar Park, located in western India city Gujarat. It has a host of plants within it (46 to be exact), including Charanka Solar Park (which would be in the top 10 largest solar plants just by itself). It has a capacity of 856 MW, and it is only getting bigger as it is still under construction. Gujarat saves around 8 million tonnes of carbon dioxide entering the atmosphere each year.

In response to a bevy of controversial energy issues emerging in the state, a coalition of gaming, tech and energy companies will align to promote more consumer choice in what’s shaping up to be a long battle against the state’s dominant power company, NV Energy.
The Nevada Coalition to Protect Ratepayers includes Switch, Wynn Resorts, Las Vegas Sands, SolarCity and Sunrun. The group’s formation follows weeks of debate about a disputed rooftop solar policy that reduces power bills for ratepayers and a 2001 law that allows large companies to generate and purchase power without the utility.
Read: Gaming, tech and solar team up to promote policy changes